Identifying the “smell” of different types of lung bacteria could lead to a simple breath test to diagnose infections, a study on mice published in the Journal of Breath Research, suggests.
Breath analysis could reduce lung infection diagnosis times from weeks to minutes, the Vermont researchers said.
Scientists have already researched breath tests to diagnose asthma and cancer.
An expert said breath analysis was “an important and emerging field”.
Diagnosing bacterial infections traditionally means collecting a sample that is used to grow bacteria in the lab. This bacteria is then tested to classify it and see how it responds to antibiotics, which can take time.
Doctors see breath analysis, in contrast, as a fast and non-invasive method of diagnosing diseases.
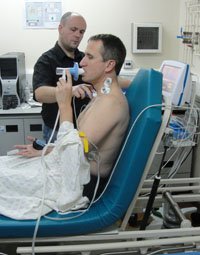
Identifying the smell of different types of lung bacteria could lead to a simple breath test to diagnose infections, a study on mice suggests
For the study, researchers from the University of Vermont analyzed volatile organic compounds (VOCs) given off in exhaled breath by different bacteria as well as different strains of the same bacterium.
They infected mice with two bacteria that are both common in lung infections – Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus – and sampled their breath after 24 hours.
The compounds in their breath were analyzed using a technique called secondary electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (SESI-MS), which is capable of detecting extremely small elements of the chemicals present in their breath.
The researchers said they found a “statistically significant” difference between the breath profiles of the mice infected with the bacteria and the mice that were uninfected.
They also said they were able to differentiate between two species of bacteria and two different strains of the same P. aeruginosa bacterium.
But Jane Hill, co-author of the study, from the University of Vermont College of Medicine, said there were still some challenges to overcome with “breath-prints”.
“We are now collaborating with colleagues to sample patients in order to demonstrate the strengths, as well as limitations, of breath analysis more comprehensively,” she said.
The toilet seat has acquired an unfair reputation as the dirtiest item in the average household, but scientists say there are far filthier places in our house, some of them where we least expect.
Would you chop your vegetables on your toilet seat? I think pretty much all of us would say No. But maybe we should think again.
Dr. Chuck Gerba, professor of microbiology at the University of Arizona, studies how diseases are transferred through the environment. This involves swabbing household items and measuring how many bacteria – and what sort – develops.
He particularly looks for faecal bacteria such as E.coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
His studies have found that on the average toilet seat there are 50 bacteria per square inch.
“It’s one of the cleanest things you’ll run across in terms of micro-organisms,” he says.
“It’s our gold standard – there are not many things cleaner than a toilet seat when it comes to germs.”
We should be more worried about other household items, it seems.
“Usually there are about 200 times more faecal bacteria on the average cutting board than on a toilet seat,” he says.
In the kitchen it doesn’t necessarily get there through actual contact with faeces. It comes via raw meat products or the viscera from inside of the animal, where a lot of the faecal bacteria originate.
Would Dr. Chuck Gerba be more inclined to chop his vegetables on a toilet seat then?
“It would seem a safer place,” he says.
“Not that I would recommend it, but you might treat your cutting board a bit more like you do your toilet seat.”
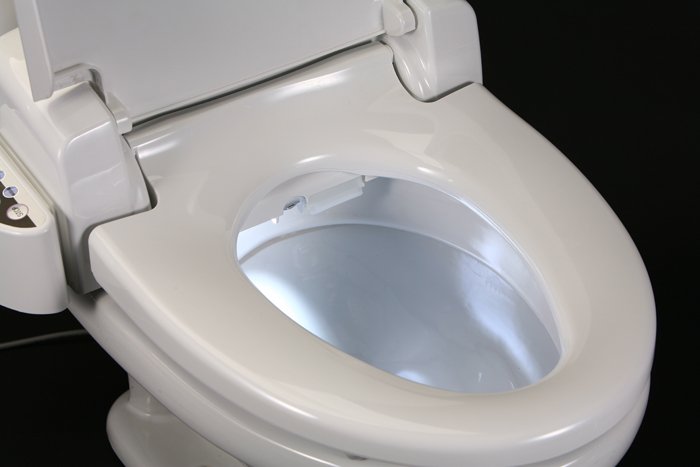

The toilet seat has acquired an unfair reputation as the dirtiest item in the average household, but scientists say there are far filthier places in our house
It’s because we all fear the dirtiness of the toilet seat so much that we regularly clean it, so perhaps this is the course of action we need to take with our chopping boards. Luckily with some of the new toilet seat technology you can at least deal with some of the smell issues through charcoal filtering, and hopefully we’ll start to see more sterilization options getting popular.But the filthiest culprit in our homes is the kitchen sponge or cloth.
According to Dr. Chuck Gerba, there are about 10 million bacteria per square inch on a sponge, and a million on a dishcloth.
In other words, a kitchen sponge is 200,000 times dirtier than a toilet seat, and a dishcloth is 20,000 times dirtier.
This is the same the world over.
“Always the dirtiest thing by far is the kitchen sponge,” says John Oxford, professor of virology at the University of London and chair of the Hygiene Council – an international body that compares hygiene standards across the world.
Its latest study examines samples from homes in nine different countries, and finds that 21% of “visibly clean” kitchen cloths actually have high levels of contamination. The cloths also fail the bacterial test which looks for E.coli.
The study identifies faecal bacteria in other places around the home, and this varies from one country to another.
Saudi Arabia has the dirtiest fridges, with 95% of the fridges in the study failing the bacteriology test for E.coli. And in South Africa, the dirtiest item is the seal in the bath, with almost two-thirds with unsatisfactory levels of E.coli and 40% for mould.
“It’s always a bit delicate which countries are the worst,” says John Oxford.
“We found that countries like Australia and particularly Canada are high up on the hygiene list… Countries near the bottom are fairly routinely, unfortunately, India and Malaysia.”
What about away from our homes? Dr. Chuck Gerba says the office is particularly bad.
“Many people don’t realize they’re talking dirty every time they pick up their phone, because they never clean it.
“The average desktop has 400 times more bacteria than on a toilet seat.”
“Shopping trolleys are really bad,” warns Chuck Gerba. What’s more, about half of reusable shopping bags have faecal bacteria in them.
“Some people have more faecal bacteria in their grocery bag than in their underwear, because they at least wash that.”
So what does this actually mean for us in terms of health risks?
“These numbers of bacteria, particularly for E.coli, are huge,” says Oxford.
“E.coli is an indicator bacterium. It may not itself cause horrible disease, but it indicates faeces is around and that might contain other organisms like salmonella and Shigella which really are virulently pathogenic.”
But we all touch these perhaps startlingly dirty things every day, and on the whole we don’t get constantly ill.
“We’re jolly lucky that as we’ve evolved over two million years, we have a whole set of genes whose only function is to get the immune system in action,” says John Oxford.
“All of us, in all these countries we have gone to, rely on Lady Luck too much, keeping our fingers crossed or sitting on our hands. In a modern scientific society, what we want is people to realize there’s a problem here and take action.”
Household hygiene
- 2010 Hygiene in the Home Study tested 180 homes in Australia, Canada, Germany, India, Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, UK and US
- Bathroom seals caused most concern, with 70% failing bacterial tests
- Fridge interiors came second – more than 40% of homes failed tests on bacteria and mould build-up
- Kitchen towels were found to be unsatisfactory or unacceptably dirty in 36% of homes
- Cleanest surface tested was pushchair with only 6% failing bacterial tests
E.coli
- Short for Escherichia coli – type of bacterium present in gut of humans and other animals
- E.coli infection happens when mutant strains are introduced to body, usually through food
- 119 people were infected during E.coli outbreak in Northern Ireland last month; 14 people died in Germany in 2011 after outbreak caused by cucumbers
Medical expert Emily Gibson has spoken out about the various health risks that come with hair removal.
Family physician Emily Gibson, who also serves as a medical director at Western Washington University in Bellingham, said that removing the hair is like creating “open wounds” that are prone to infection and even sexually-transmitted disease, such as herpes, if in contact with another person.
She added that men are at risk of infection just as much as women.
In an article she wrote for KevinMD.com, she explained “that irritation is combined with the warm moist environment” and therefore becomes a breeding ground for infection.
Dr. Emily Gibson pinpointed A streptococcus, which, in extreme cases, can lead to organ failure, and staphylococcus aureus, which can cause pimples and boils as well as far more serious side effects, in particular.
She added that “freshly-shaved areas are also more vulnerable to herpes infections due to the microscopic wounds being exposed to virus”.
Emily Gibson said that she has seen cellulitis, a soft tissue bacterial infection.
“No matter what expensive and complex weapons are used – razor blades, electric shavers, tweezers, waxing, depilatories, electrolysis – hair, like crab grass, always grows back and eventually wins,” Dr. Emily Gibson wrote in the report.
“In the mean time, the skin suffers the effects of the scorched battlefield,” she continued.
The Independent reported that hair removal cost Americans $2.1 billion in 2011.
Despite the health risks, Dr. Emily Gibson noted the practice’s popularity: “The amount of time, energy, money and emotion both genders spend on abolishing hair some areas is astronomical.
“The hair removal industry, including medical professionals who advertise their specialty services to those seeking the <<clean and bare>> look, is exponentially growing.”


